Three Focuses in the NR Market in Q1, 2018
1. NR Prices Slumped Twice in Q1
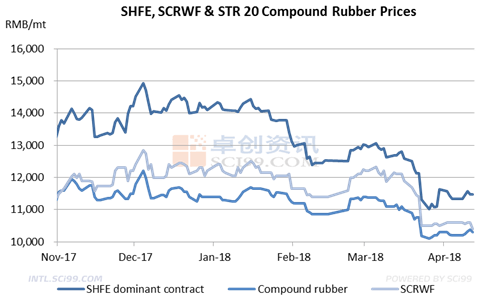
As can be seen from the chart above, NR prices kept fluctuating within a small range from December 2017 to mid-January 2018. After that, NR prices showed a downtrend. In late January and early February, the NR dominant contract price at the SHFE dropped from over RMB 14,000/mt to below RMB 13,000/mt. The main reason was the high inventories and the decreasing demand. Before the Spring Festival, most tire producers stopped the stock-up of rubber feedstocks. In the futures market, the high open interest and the low trading volume also meant that the spread between the NR futures price and the spot price needed to be narrowed.
In late March, the NR futures price slumped again, which was also mainly affected by the imbalance between the supply and the demand. The NR inventory at the Qingdao Bonded Area remained high. The rubber tapping in Yunnan also started gradually. So the NR supply faced an uptrend. The tire market was recovering slowly, and the operating rate at the tire producers was stable at around 70%. Feedstock stocks at tire producers could maintain production for 15-40 days. So the tire producers were less active in feedstock replenishment.
2. NR Inventories Remained High
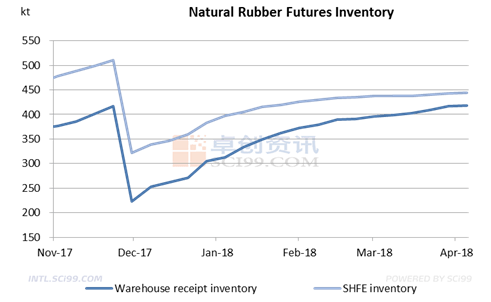
As can be seen from the chart above, the NR futures inventory showed an uptrend from December 2017 to April 2018. According to the weekly inventory report which was newly issued by the SHFE, up to April 4, the inventory of the NR warehouse receipts increased to 418,810mt, and the total inventory was 444,611mt. In early January, the inventory of the NR warehouse receipts was 313,280mt and the total inventory was 396,860mt. The inventory increase slowed down from mid-February, as the stock was almost full. There was a newly added 15kt stock in Qingdao.
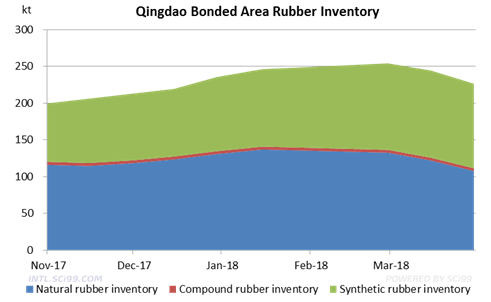
Up to April 3, 2018, the total rubber inventory at the Qingdao Bonded Area was 226.4kt, down 1.8kt or 7.3% from mid-March. The NR ex-warehouse volume increased. The inventories of both NR and synthetic rubber dropped, but they were still high. The inventory out of the bonded area was heard to be around 260kt, and the stock capacity was still tight. Although the ex-warehouse volume increased, it was still lower than the stock-in volume. The NR inventory decreased slightly, which was mainly affected by the NR import volume decline and the consumption of the resources. As the inventory was still high, it was still uncertain that whether it would drop in the future.
3. Thai Government May Prolong NR Export Limitation
Thai government held firm to the NR export limitation. According to Thai Customs, the NR (including NR latex and mixed rubber) export volume in Thailand was 427.2kt in February 2018, down 0.3% M-O-M and down 6.02% Y-O-Y. The export volume of mixed rubber was 104.3kt, up 23% Y-O-Y and down 9% M-O-M. The export volume of NR latex was 131.3kt, up 31.3% Y-O-Y and up 29.11% M-O-M.
Thai government issued the NR export limitation policy which was implemented from January to March 2018. It had a firm determination on the NR export limitation. According to sources, the export limitation volume had been announced to the NR (standard rubber and sheet rubber) processing plants. In Q1, 2018, Thai government required the NR exporters to lower 20% of the average Q1 export volume in 2016 and 2017. The export limitation policy mainly affected the export of standard rubber and ribbed smoked sheet. The export of NR latex suffered few influences. With the export limitation policy, export orders at the rubber feedstock processing plants were impacted. The rubber inventories were high at the plants.
As a solution, Thai cabinet agreed to allot 2 billion THB from the annual budget to promote the NR consumption by the official departments. The Rubber Authority of Thailand (RAOT) would use the money to purchase NR resources during the tapping season in 2018. SCI learnt that Thai government might prolong the NR export limitation policy in the future.
Forecast
As for the supply, the rubber tapping in Yunnan and Hainan will add the supply of Chinese-made NR. The rubber tapping in Southeast Asia may cause potential oversupply. NR inventories are still high in China. As for the demand, the operating rate at the Chinese tire producers hovers at around 72%. The tire market is recovering slowly. The imbalance between the supply and the demand may still remain in the short run. However, the feedstock stocks at the tire producers may drop in the future. If China’s NR import volume is still decreasing, the NR inventories will face a downtrend. Besides, NR prices are at a relatively low level, and the production cost may support NR prices to some extent. Thus, NR prices may move sideways in the short run.
Source: http://intl.sci99.com/n/4/543610.html



























